GELEBART Lionel, Engineer - Researcher, CEA Saclay/DEN/DMN/SRMA : lionel.gelebart at cea.fr
Development and organization
DEROUILLAT Julien, Engineer - Researcher, Maison de la Simulation : julien.derouillat at cea.fr
HPC support
DOUCET Nicolas Internship (12 months) at CEA Saclay/DEN/DMN/SRMA :
The first version of the code!
OUAKI Franck, Post-doctoral (19 months) at CEA Saclay/DEN/DMN/SRMA :
Extension to Finite Strains
MARANO Aldo, PhD (36 months) at CEA Saclay/DEN/DMN/SRMA and Mines-ParisTech :
Introduction of composite voxels
Definition of a general framework for couplings (application to strain gradient plasticity)
DUVERGE Jérémy, Internship (6months) at CEA Saclay/DEN/DMN/SRMA :
Additional work on composite voxels (focus on I/O)
CHEN Yang, as a post-doc at IMT Lille-Douai (France), then at Oxford University (UK)
Implementation of the phase field model for damage (from Miehe’s work)
BOIOLI Francesca, as a post-doc at LEM-ONERA (France)
Coupling between AMITEX and the DD code microMegas http://zig.onera.fr/mm_home_page/
BOISSE Julien, reseracher at Université de Lorraine (France)
Preliminar implementation of various metallurgical phase field models (proofs of concept)
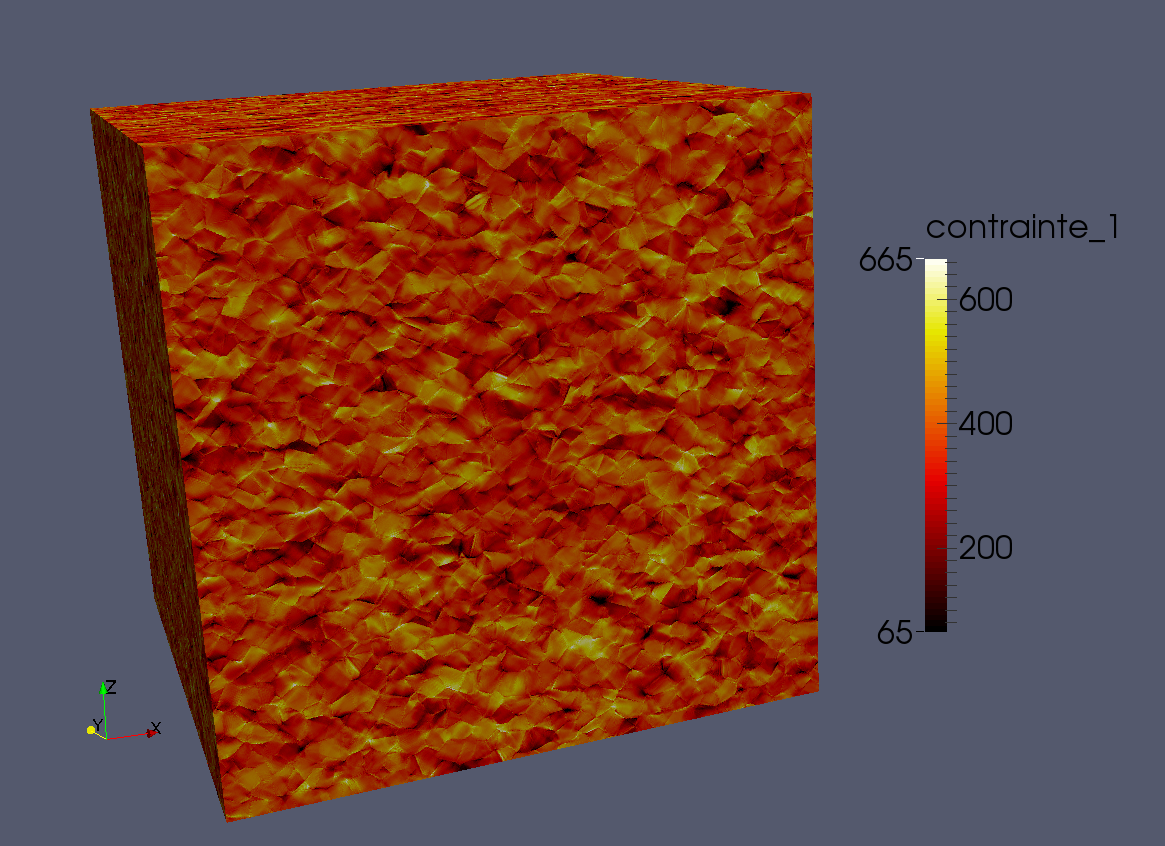
AMITEX_FFTP is a distributed solver based on FFTs for non-linear mechanical simulations on heterogeneous unit-cells (described by regular 3D images). AMITEX_FFTP can be run either on individual PC, local clusters or on large High Performance Computing platforms to perform large scale simulations such as the example given in the figure below.
Since recent developments, the usage of AMITEX_FFTP can now be divided into two parts :
The purpose of the further developments are now to :
AMITEX_FFTP is written in modern FORTRAN and relies on the 2DECOMP&FFT library (http://www.2decomp.org) that provides:
For the user interface, the reading of XML files in AMITEX_FFTP relies on FoX (http://www1.gly.bris.ac.uk/~walker/FoX/) a Fortran library for XML.
FoX and 2DECOMP&FFT have been added to the source files of AMITEX_FFTP, external libraries are required:
The user interface of AMITEX_FFTP allows to:
The mechanical FFT-based solver within AMITEX_FFTP allows to:
The mechanical behavior law is evaluated within a standard UMAT procedure which ensures compatibility with both:
Of course, the UMAT procedure coming from ABAQUS, a good compatibility is also expected with this FE code.
Finally, if the code mainly focuses on mechanics, stationary diffusion problems can be solved on unit-cells with prescribed average flux or gradient.